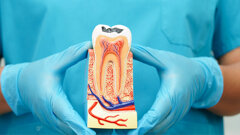
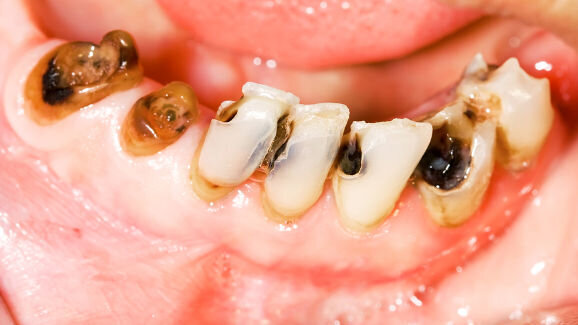
LONDON, UK: Despite worldwide efforts to improve oral health, a global study has found that 35 per cent of the world’s population currently suffer from untreated carious lesions in their permanent teeth. It also established that 621 million children worldwide have tooth decay that goes without dental care.
To make things worse, hundreds of millions of new cases are expected to add to the burden of dental decay annually owing to neglected treatment, according to the new paper by researchers from the UK, the US and Australia published online in the Journal of Dental Research.
Even developed countries are affected, with one in three people in the UK suffering the consequences of neglected treatment, along with one in five in the US, for example.
The findings, which are part of the latest Global Burden of Disease study, involved a systematic review of all data on untreated dental decay, leading to a comprehensive report on rates of tooth decay for all countries and age groups and both sexes for 1990 and 2010. The team analysed 192 studies of 1.5 million children aged 1 to 14 years old, across 74 countries, and 186 studies of 3.2 million people aged 5 years or older, across 67 countries.
“We have seen a clear shift in the burden of tooth decay from children to adults. The current perception that low levels of decay in childhood will continue throughout life seems incorrect,” said lead author Prof. Wagner Marcenes from the Queen Mary University of London. “It is alarming to see prevention and treatment of tooth decay has been neglected at this level because if left untreated it can cause severe pain, mouth infection and it can negatively impact children’s growth.”
Marcenes explained that the study underscores the vital need to develop effective oral health promotion strategies.
“The fact that a preventable oral disease like tooth decay is the most prevalent of all diseases and injuries examined in our report is quite disturbing and should serve as a wake-up call to policymakers to increase their focus on the importance of dental health,” he continued. “Extending oral health promotion activities to the work environment is necessary to maintain good oral health to reduce the major biological, social and financial burden on individuals and healthcare systems.”
Tooth decay is the fourth most expensive chronic disease to treat, and studies have shown that if left untreated it can lead to poor productivity at work and absenteeism in adults and poor school attendance and performance in children.
EDINBURGH & GLASGOW, UK: Brushing twice a day is usually considered the most effective measure to maintain oral health in children. New research in ...
EDINBURGH, UK: A study by researchers at the University of Edinburgh has shown that a natural chemical related to those found in liquorice root could help ...
The global dental composites market is anticipated to grow, due to changes in diet and lifestyle, and a rapidly growing geriatric population across the ...
SHEFFIELD, UK: According to British scientists, the dentition of puffer fish could provide a new model for understanding the genetic processes underlying ...
DUBLIN, Ireland: Work on more than a dozen new primary care health centres across Ireland began last week after the European Investment Bank (EIB) ...
NORTHAMPTON, UK: Since mid-June, dental clinics across the UK have faced a staggered resumption of elective dental care after the easing of a ...
NEWCASTLE UPON TYNE, England: The systematic and oral health effects of smoking are well established, including reduced calcium absorption, altered vitamin ...
LONDON, UK: In celebration of World Oral Health Day, representatives of the FDI World Dental Federation presented the latest findings on oral health on 20 ...
Artificial intelligence (AI) has moved from theory into daily prosthodontic practice, reshaping diagnosis, treatment planning and design workflows. My ...
Live webinar
Tue. 24 February 2026
6:00 pm UTC (London)
Prof. Dr. Markus B. Hürzeler
Live webinar
Tue. 24 February 2026
8:00 pm UTC (London)
Prof. Dr. Marcel A. Wainwright DDS, PhD
Live webinar
Wed. 25 February 2026
4:00 pm UTC (London)
Prof. Dr. Daniel Edelhoff
Live webinar
Wed. 25 February 2026
6:00 pm UTC (London)
Live webinar
Thu. 26 February 2026
1:00 am UTC (London)
Live webinar
Tue. 3 March 2026
4:00 pm UTC (London)
Dr. Omar Lugo Cirujano Maxilofacial
Live webinar
Wed. 4 March 2026
1:00 am UTC (London)
Dr. Vasiliki Maseli DDS, MS, EdM



 Austria / Österreich
Austria / Österreich
 Bosnia and Herzegovina / Босна и Херцеговина
Bosnia and Herzegovina / Босна и Херцеговина
 Bulgaria / България
Bulgaria / България
 Croatia / Hrvatska
Croatia / Hrvatska
 Czech Republic & Slovakia / Česká republika & Slovensko
Czech Republic & Slovakia / Česká republika & Slovensko
 France / France
France / France
 Germany / Deutschland
Germany / Deutschland
 Greece / ΕΛΛΑΔΑ
Greece / ΕΛΛΑΔΑ
 Hungary / Hungary
Hungary / Hungary
 Italy / Italia
Italy / Italia
 Netherlands / Nederland
Netherlands / Nederland
 Nordic / Nordic
Nordic / Nordic
 Poland / Polska
Poland / Polska
 Portugal / Portugal
Portugal / Portugal
 Romania & Moldova / România & Moldova
Romania & Moldova / România & Moldova
 Slovenia / Slovenija
Slovenia / Slovenija
 Serbia & Montenegro / Србија и Црна Гора
Serbia & Montenegro / Србија и Црна Гора
 Spain / España
Spain / España
 Switzerland / Schweiz
Switzerland / Schweiz
 Turkey / Türkiye
Turkey / Türkiye
 UK & Ireland / UK & Ireland
UK & Ireland / UK & Ireland
 International / International
International / International
 Brazil / Brasil
Brazil / Brasil
 Canada / Canada
Canada / Canada
 Latin America / Latinoamérica
Latin America / Latinoamérica
 USA / USA
USA / USA
 China / 中国
China / 中国
 India / भारत गणराज्य
India / भारत गणराज्य
 Pakistan / Pākistān
Pakistan / Pākistān
 Vietnam / Việt Nam
Vietnam / Việt Nam
 ASEAN / ASEAN
ASEAN / ASEAN
 Israel / מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל
Israel / מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל
 Algeria, Morocco & Tunisia / الجزائر والمغرب وتونس
Algeria, Morocco & Tunisia / الجزائر والمغرب وتونس
 Middle East / Middle East
Middle East / Middle East










































To post a reply please login or register